Best Paper Award Nominees
one paper will be awarded on Lunch, Friday, 15thE-Health
Location-based Smartwatch Application for People with Complex Communication Needs
Marin Vuković, Željka Car, Melita Fertalj and Ida Penezić (University of Zagreb, Croatia); Valerija Miklaušić (Vienna University of Technology, Austria); Jasmina Ivšac (University of Zagreb Faculty of Education and Rehabilitation Sciences, Croatia); Nina Pavlin-Bernardić (University of Zagreb Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences, Croatia); Lidija Mandić (University of Zagreb Faculty of Graphic Arts, Croatia)
 One of the important elements of successful parenting is care for children’s safety, which includes parental knowledge about children’s whereabouts, especially when a child has complex communication needs. In this context smartwatch may become a new aid not only for children but for all persons with complex communication needs, primary due to location and communication functions which can be efficiently deployed within smartwatch application, combined with everyday habit of wearing a watch on the wrist. Innovative functions and applications may put the smartwatch in the category of safety products within assistive technology, but there is a lot to investigate since the smartwatch technology is advancing very quickly. The paper presents multidisciplinary research performed in the area of information and communication technology, focusing on a smartwatch application as the assistive technology for locating persons with complex communication needs. Developed software application is described, that is based on the concept of predefined and ad hoc safety zones, enabling smartphone mobile application and web application users to define the zones for safe movement of smartwatch wearer. Also the graphical issues related to the smartwatch user interface design and other smartwatch performances that were faced during the research are presented.
One of the important elements of successful parenting is care for children’s safety, which includes parental knowledge about children’s whereabouts, especially when a child has complex communication needs. In this context smartwatch may become a new aid not only for children but for all persons with complex communication needs, primary due to location and communication functions which can be efficiently deployed within smartwatch application, combined with everyday habit of wearing a watch on the wrist. Innovative functions and applications may put the smartwatch in the category of safety products within assistive technology, but there is a lot to investigate since the smartwatch technology is advancing very quickly. The paper presents multidisciplinary research performed in the area of information and communication technology, focusing on a smartwatch application as the assistive technology for locating persons with complex communication needs. Developed software application is described, that is based on the concept of predefined and ad hoc safety zones, enabling smartphone mobile application and web application users to define the zones for safe movement of smartwatch wearer. Also the graphical issues related to the smartwatch user interface design and other smartwatch performances that were faced during the research are presented.
Smart City/Environment
An Internet of Sport Architecture Based on Emerging Enabling Technologies
Luca Mainetti, Luigi Patrono, Maria Laura Stefanizzi (University of Salento, Italy)
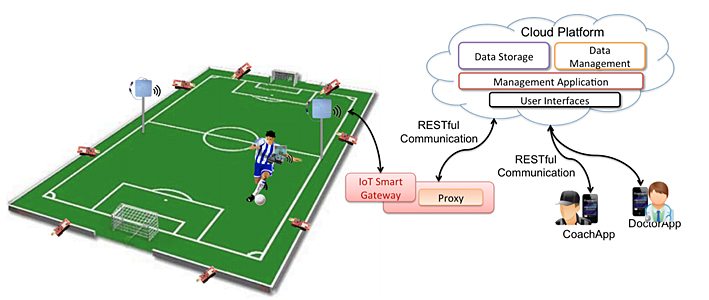 Sports and recreational activities provide an interesting domain of research that includes several of the critical challenges for next generation of services. The adoption of emerging Internet of Things technologies into the field of sport could significantly improve the sport experience and also the safety level of team sports. To this purpose, this paper presents a novel Sport System based on the jointly use of different technologies, such as RFID, WSN, Cloud, and mobile. It is able to collect, in real time, both environmental parameters and players’ physiological data via an ultra-low-power Hybrid Sensing Network (HSN) composed of 6LoWPAN nodes integrating UHF RFID functionalities. Sensed data are delivered to a Cloud platform where a monitoring application makes them easily accessible via REST Web Services. A simple proof of concept has demonstrated the appropriateness of the proposed system. This work represents a first real attempt to demonstrate the benefits introduced by the use of IoT technologies in sport environments.
Sports and recreational activities provide an interesting domain of research that includes several of the critical challenges for next generation of services. The adoption of emerging Internet of Things technologies into the field of sport could significantly improve the sport experience and also the safety level of team sports. To this purpose, this paper presents a novel Sport System based on the jointly use of different technologies, such as RFID, WSN, Cloud, and mobile. It is able to collect, in real time, both environmental parameters and players’ physiological data via an ultra-low-power Hybrid Sensing Network (HSN) composed of 6LoWPAN nodes integrating UHF RFID functionalities. Sensed data are delivered to a Cloud platform where a monitoring application makes them easily accessible via REST Web Services. A simple proof of concept has demonstrated the appropriateness of the proposed system. This work represents a first real attempt to demonstrate the benefits introduced by the use of IoT technologies in sport environments.
ENERGY
Energy Harvester for Smart Sensors Systems
Leonardo Pantoli, Alfiero Leoni, Vincenzo Stornelli, GIuseppe Ferri (University of L’Aquila, Italy)
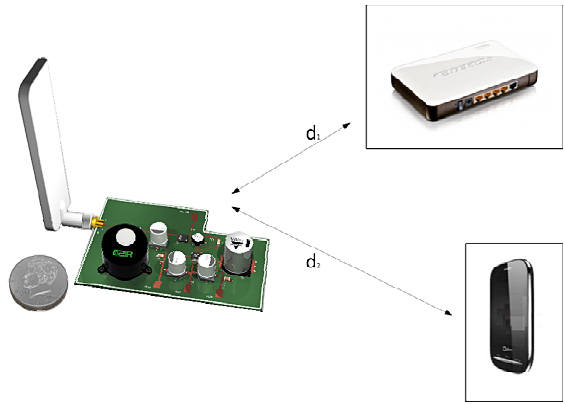 We present a high dynamic range and high efficiency energy harvesting system. The designed circuit is a dual band architecture able to capture the largest amount of EM radiation in the urban environment being tuned both at GSM and WiFi operating frequencies. The system handles, with a high conversion efficiency, an incoming power typically ranging from -20dBm to 20dBm and rectifies it into a DC voltage source. Test measurements of the proposed system have confirmed all expectation making the proposed solution suitable to be used in several commercial urban remote low power sensor networks applications as those for buildings monitoring.
We present a high dynamic range and high efficiency energy harvesting system. The designed circuit is a dual band architecture able to capture the largest amount of EM radiation in the urban environment being tuned both at GSM and WiFi operating frequencies. The system handles, with a high conversion efficiency, an incoming power typically ranging from -20dBm to 20dBm and rectifies it into a DC voltage source. Test measurements of the proposed system have confirmed all expectation making the proposed solution suitable to be used in several commercial urban remote low power sensor networks applications as those for buildings monitoring.
